Proper cannabis knowledge is crucial to the understanding of how cannabis will affect your body.
Our goal at The WellFlower is to provide information to each patient that will allow them to make educated decisions when creating a personalized health regimen that will work best for their needs.
The Cannabis Plant
COLA: The main part of the flower; contains many small floral clusters.
BRACTS: Small leaves that surround the reproductive cells of a female weed plant.
TRICHOMES: Hairlike appendages found on the surface of the cannabis plant that protect the plant. These trichomes contain resinous glands that create flavonoids, cannabinoids, & terpenes.
NODE: The point in which the stem & leaf intersect. This is important in determining the sex o the marijuana plant, which in turn is crucial to the final product.
FAN LEAVES: Large, protruding leaves that appear along the length of the plant.
SUGAR LEAVES: Small leaves found throughout the cannabis colas’ cupping buds. These leaves have a high volume of trichomes found on them, which makes it look like they are covered in sugar. The trim from these leaves can be used to make edibles or concentrates.
STEM: This is the main support structure of the plant, which transports fluids, nutrients & information from the roots to the rest of the plant.
PISTIL: Female flower’s reproductive system.
STIGMA: Thin hairs from the female’s bract to catch male pollen.
Cannabis Sativa & Cannabis Indica
When it comes to the cannabis plant, there are two major types. They are called Cannabis Sativa & Cannabis Indica. Each strain offers its own range of effects on the mind & body resulting in a wide range of medicinal benefits.
Cannabis Sativa
Cannabis Sativa plants are on average the taller & less bushy of the two plant types. The terpene profile & cannabinoid composition of Sativa strains are known to be very pungent. Cannabis Sativa will generally contain a higher concentration of THC compared to Indica strains. Cannabis Sativa is known for its stimulating mental effects that help users feel more focused & motivated, because of this its best suited for daytime use & social situations.
Reported Effects Include:
Uplifting
Focus
Energy
Creativity
Motivation
Cannabis Indica
Cannabis Indica strains originated near Central Asia. Indica strains are known for producing high quantities of resin, which some say were an adaptation for protection against harsh weather conditions. Cannabis Indica is known to have more of a body, sedative effect versus the stimulating mind/mental effects of Sativa.
Reported Effects Include:
Sleepy
Stoney
Physically Soothing
Anti-Stress
The Endocannabinoid System
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system identified in the 1990’s. The ECS system plays a role in regulating multiple functions such as sleep, appetite, memory, & fertility. There are three core components of the system: endocannabinoids, receptors, & enzymes.
Endocannabinoids are molecules made by your body. Two key endocannabinoids are Anandamide & 2-AG, which help to keep internal functions running smoothly. The body will produce these endocannabinoids as needed.
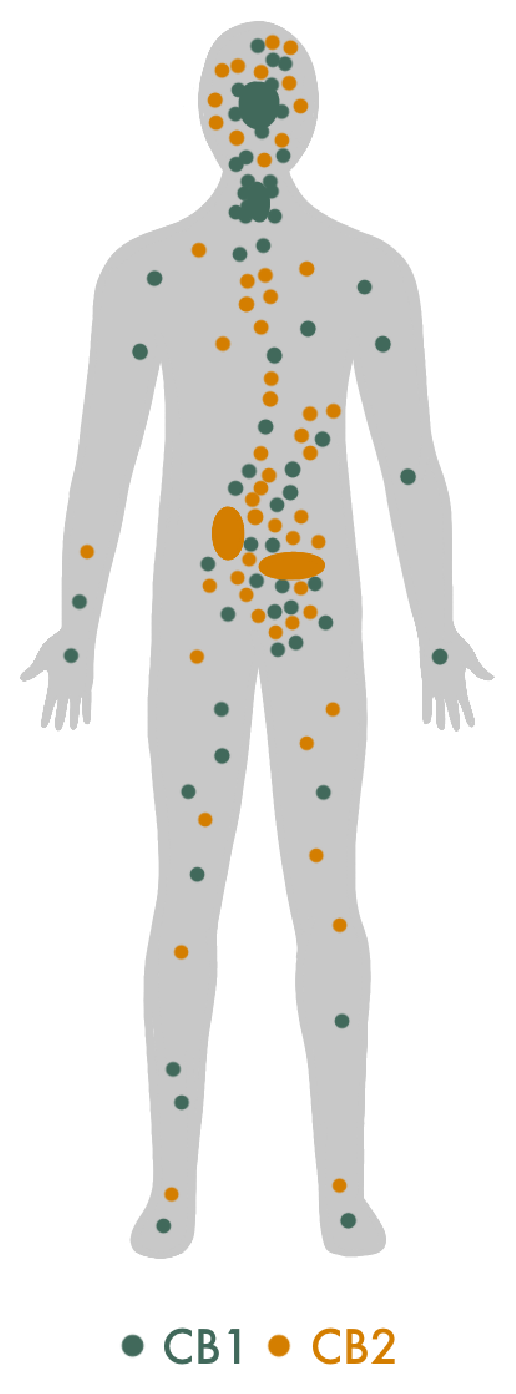
Endocannabinoid receptors are receptors that endocannabinoids bind to in order to signal to the body that the endocannabinoid system needs to take action. There are two main endocannabinoid receptors, CB1 (found in the central nervous system) and CB2 (found in the peripheral nervous system). The effects that will result depend on where the receptor is located and which endocannabinoid it binds to.
THC vs
CBD
There are two major natural compounds that are found in cannabis plants, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) & we are here to help you understand them.
THC is the cannabinoid molecule that interacts mainly with the CB1 receptors found primarily in our brains that produce experienced effects like euphoria & pain reduction.
CBD is the cannabinoid molecule that interacts mainly with the CB2 receptors found primarily in our gut and immune cells. It does not produce any psychoactive effects, but it can be helpful controlling inflammation & seizures.
Medical Benefits
Both CBD & THC can provide relief from many of the same conditions, & both are worth exploring when creating your personal health regimen.
Storage
Cannabis degrades when exposed to light, oxygen, & high temperature. Place your cannabis in a light & oxygen tight container & store it in a cool area.
THC
CBD
THC Uses:
Low Appetite
Muscle Spasms
Nausea
Chronic Pain
THC Side Effects:
Coordination Issues
Dry Mouth
Increased Heart Rate
Memory Loss
Red Eyes
Slowed Reaction Times
CBD Uses:
Depression
IBS (Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
Inflammation
Mental Disorders
Migraine
Nausea
Pain
CBD Side Effects:
Appetite Changes
Diarrhea
Dizziness
Fatigue
Weight Loss
Since both THC & CBD offer medical benefits with potential side effects, exploring both options to create a regimen that responds well to your body’s needs is highly encouraged.
Methods of Administration
Transdermal
Dermatological administration can be a very effective way of using cannabis. Creams are great for localized pain control, like pain in joints.
Ingestion
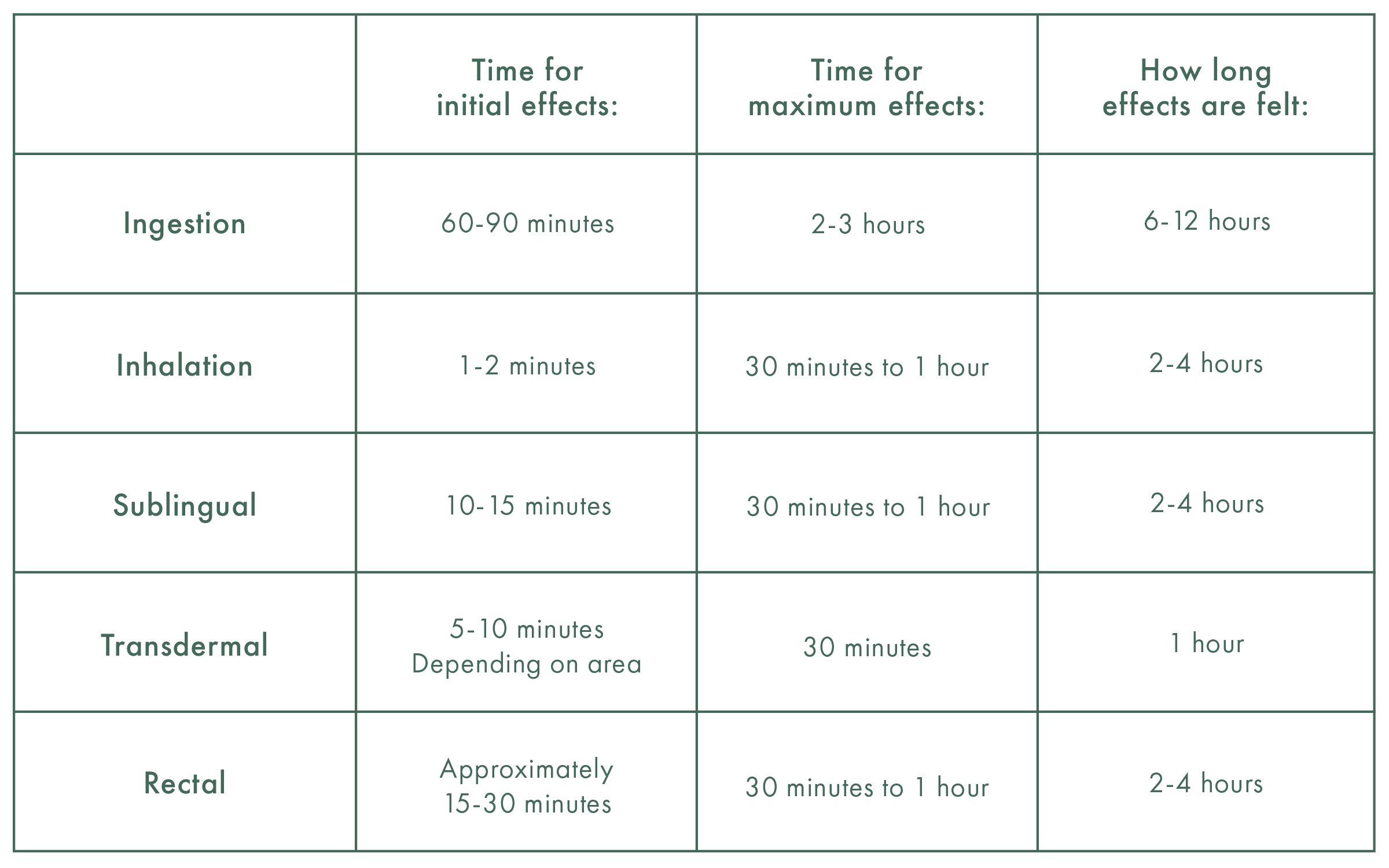
When swallowed the cannabinoids go from the gut into the liver first, then into the bloodstream. This process is responsible for the prolonged symptom control of edibles. Maximum effect is 2-3 hours after eating.
Inhalation
Inhalation is the fastest acting method of administration. A patient can get an effect within minutes with maximum effect after 30 minutes.
Sublingual
Sublingual administration is a good way for a patient to introduce cannabis into their body. The desired amount of cannabis is placed under the tongue but not swallowed for 2-3 minutes.
Rectal/Suppositories
A suppository is an effective way of introducing cannabis into a patient’s body because of the absorption in the lower colon.
Layering Methods of Administration
Layering the methods of administration is a very important concept. The way one introduces cannabis into their body plays a role in the effect produced. By layering different cannabis products, one takes advantage of the time & duration of desired effect, thus increasing & sustaining symptom control.
Dosing & Titration
The mantra for dosing & titration is “start low & go slow”. By starting with a small dose one can test the effects on the body & condition being treated. Through titration, the process of take small incremental steps, a patient can reach their desired goals with minimal side effects.
Tolerance
Tolerance to medical cannabis does develop, therefore, for every symptom for which you are using medical cannabis, you should try to find at least 2-4 different strains or products, that all alleviate that same symptom. When tolerance seems to have developed, you can potentially turn to a different strain. Additionally, if cannabis use is stopped for approximately 5-7 days, the tolerance will diminish to almost zero for most users.
Overconsumption Strategies
Biologically, cannabis is an extremely safe substance. According to the CDC (Centers for Disease Control), there have not been any reported deaths resulting solely from cannabis use.
Unlike other drugs, excessive use of cannabis does not lead to an overdose and/or death, however it is possible to overindulge and experience side effects. It is important to remember that because each person is unique, the reaction that each person has to cannabis is different.
Some effects of overindulgence are:
Nausea & vomiting
Extreme confusion
Paranoia
Loss of judgement & motor control
Increased blood pressure
If cannabis is consumed in addition to any other substance, such as alcohol, you increase your risk of experiencing the symptoms listed above.
The good news is there are some strategies that are known to help until the unwanted effects wear off:
1. Start with small doses. For example, start with a small inhalation, wait 20-30 minutes, & evaluate how you feel before inhaling again.
2. Introducing CBD through fast acting administration methods (inhalation/sublingual). There is a competitive inhibition at the receptor level that decreases the effects of THC, thus decreasing the negative symptoms.
3. Change your environment - find a safe, quiet space to relax until side effects have subsided.
4. Keep drinking water to stay hydrated.
The above contains general medical information. The medical information is not advice & should not be treated as such. Marijuana can impair concentration, coordination, & judgement. Do not operate a vehicle or machinery under the influence of this drug. For use only by adults twenty-one & older.
Medical Cannabis Patient Knowledge
Michigan residents with approved conditions (or their caregivers) can apply to the Michigan Medical Marijuana Program (MMMP) for a Registry ID card, valid for 2 years. The application must include a Physician Certification form, completed & signed by a Medical Doctor or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine & Surgery who is fully licensed by the State of Michigan. The state also requires a patient/doctor relationship. We require our patients to follow up yearly.
An ID card provides protections for the medical use of marijuana, but there are still rules and laws to follow. By staying legal & following the laws provided, not only do you protect your right to safely use medical marijuana, but you also help keep it legal for others.
Medical Cannabis Responsibilities
Must keep written log:
a. Strains of cannabis used
b. Method of administration
c. Dose
d. EffectMust locate a licensed provisioning center with test medications
No travel with cannabis in airports or across state lines
For each qualifying patient to whom they are connected through the department’s registration process, a combined total of 2.5 oz of usable cannabis & usable cannabis equivalents.
When traveling- all medication should be in a lockbox placed in the trunk of the car or as far away from the driver as possible.